Intune: Endpoint Protection
Whilst Endpoint Protection can be suitably managed for traditional Active Directory-joined devices using Group Policies, you'll need an alternative to protect your Azure AD joined devices. Luckily Intune can do this for us by way of a device configuration profile.
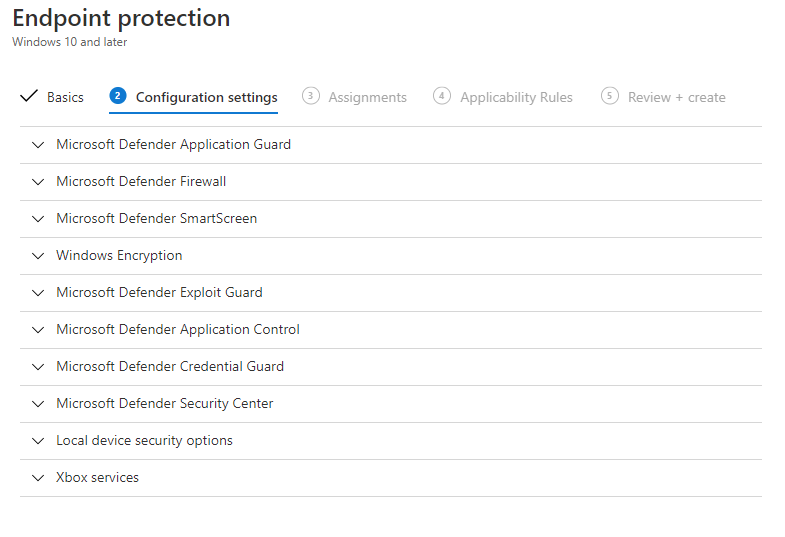
Go to Intune > Devices > Configuration Profiles and click on Create profile. Select Windows 10 and later as the platform, and Endpoint protection. Once you've filled out the basic detail, you'll see a large selection of things we can manage. I'll go through these one at a time.
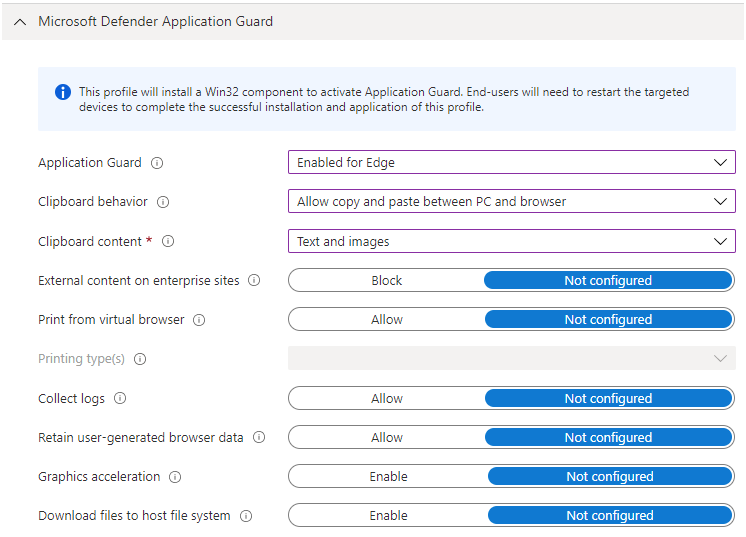
Application Guard
Application Guard isolates untrusted websites from the local computer by running them in a virtualised container, meaning that any exploits that happen to be on the untrusted website will not have access to corporate data or to the local device. It also works for Microsoft Office - preventing untrusted Word, Excel and PowerPoint files from accessing the local device - protecting it if the untrusted file contains, for example, malicious macros. You can find out more about Application Guard on the Microsoft Docs pages. Only the Edge version of this can be configured from Intune so let's have a look at that now.
In order to define which sites you want to be forced to use Application Guard, you need to define a network boundary. If you don't define the network boundary, the user will be able to launch an Application Guard window when required by clicking on the menu in Edge, in the same way as they would do if they had enabled Application Guard manually on a home PC. This protection applies to both Edge Legacy and the new Chromium-based Edge.
The system requirements for running this are:
- Windows 10 Enterprise (1709 or higher) or Education (1903 or higher), 64 bit. Professional Edition can run Application Guard but it can't be managed by Intune.
- Browser: Edge. IE also supports Application Guard but it doesn't look like you can control this from Intune (and it shouldn't be used as it's outdated)
- 64 bit CPU with at least 4 cores, with support for virtualization extensions - SLAT and VT-x (Intel) or AMD-V (AMD)
- VT-d (Intel) or AMD-Vi (AMD) I/O Memory Management Unit support (not required but strongly recommended)
- At least 8GB RAM
Further Reading:
- Create a Windows Network Boundary profile in Microsoft Intune - Azure | Microsoft Docs
- Microsoft Defender Application Guard (Windows 10) - Windows security | Microsoft Docs
- WindowsDefenderApplicationGuard CSP - Windows Client Management | Microsoft Docs
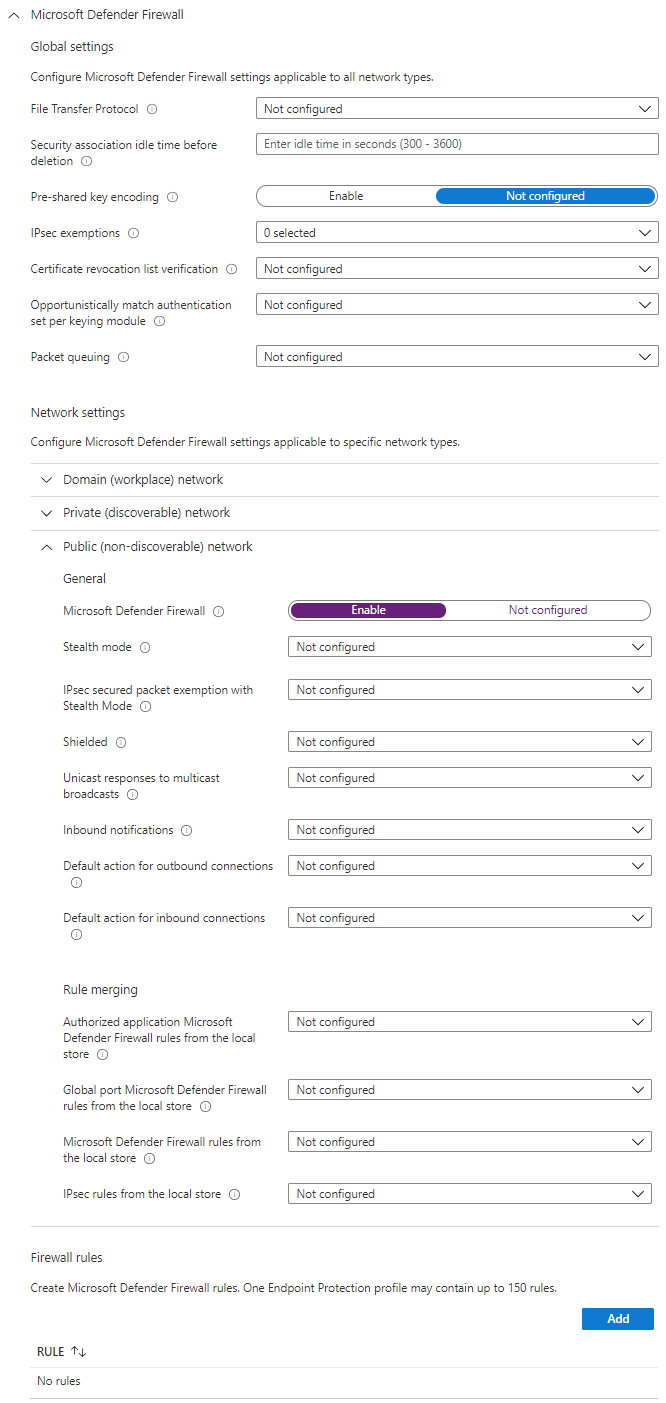
Defender Firewall
We can configure Defender Firewall (previously known as Windows Firewall) through Intune. There's a lot of settings that can be configured here:
- Global settings - disable FTP, and some certificate and IPSec settings
- Profile settings - Domain/Private/Public
- Toggle the firewall on/off
- General settings for the profile - Stealth mode, Shielded, notifications and default action for inbound/outbound connections.
- Rule merging settings
- Table of firewall rules which you can define.
- Toggle the firewall on/off
Defender SmartScreen
SmartScreen helps protect the user and device against phishing or malware websites and programs. It does this by looking for suspicious behaviour or activity in websites that the user is visiting, and will show a warning page in the event of suspicious activity. There's also a list of reported phishing sites and malicious software sites which it will check against.
SmartScreen will also perform checks on downloaded files - for example comparing against a list of malicious software, and it will also warn if the downloaded file isn't on a list of well known software.
There's not much to configure here in Intune - there's a lot more control over this in Group Policy - basically it's On or Off, and you can choose whether users are allowed to bypass the warning message on unverified files or not.
Further Reading:
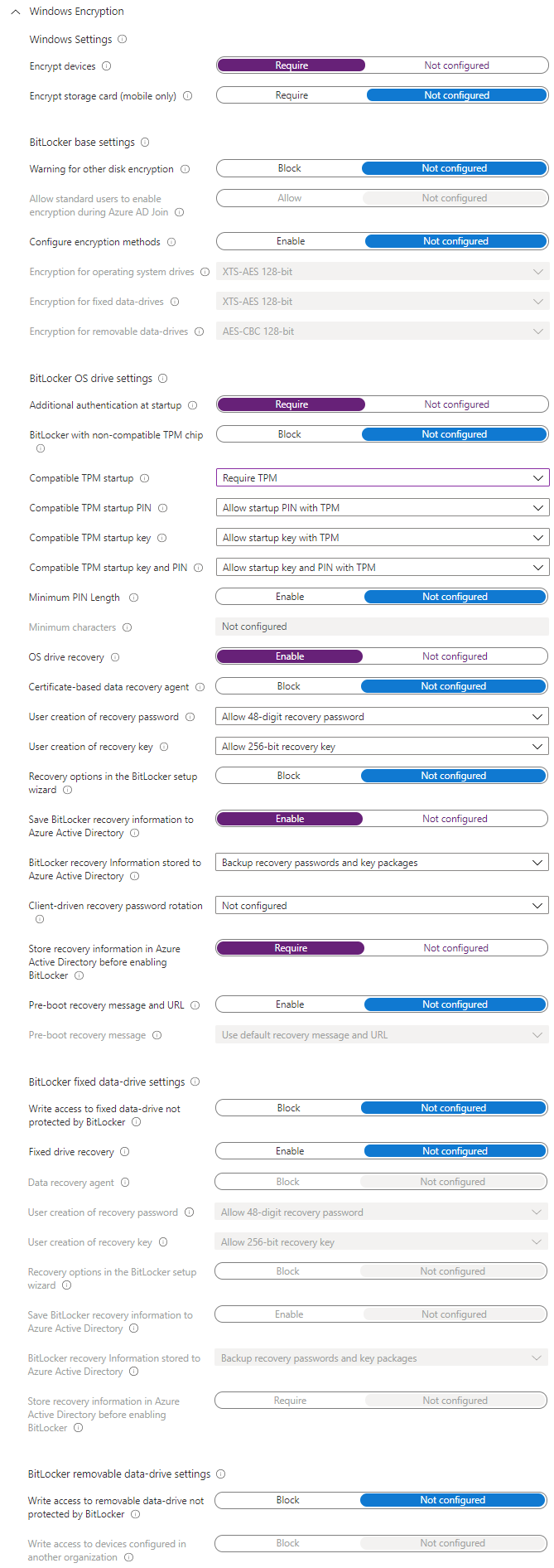
Windows Encryption
As you'd expect, Windows Encryption is the section for configuring Bitlocker. There's a range of settings that can be configured here, most of them self-explanatory. To run through the basics, enabling drive encryption, specifying authentication methods (TPM, PIN etc) and requiring recovery keys, plus configuring to store these in Azure AD, for both OS disks and other fixed disks. On top of that there's a bit on removable storage - the basics here, make it read-only until it is protected.
A fully detailed look at what Bitlocker is and how it works can be found in the Microsoft Docs.
Exploit Guard
Exploit Guard helps protect your data from attack via the applications that your users are running. It's got four parts:
- Attack Surface Reduction - This helps prevent attacks via things such as Office macros, obfuscated JavaScript/VB Script/macros and email, mostly through preventing them from launching new processes and injecting into other processes. You can exclude files and folders from protection if needed.
- Controlled Folder Access - This helps prevent against things like ransomware and other malware by preventing applications behaving in a suspicious behaviour from making changes to the contents of a specified list of folders.
- Network Filtering - Blocks outbound traffic from any application to any low reputation IP address or domain. This can be enabled, disabled or put into audit mode so you can see if anything is impacted before enabling it fully.
- Exploit Protection - Configure settings to help protect applications from exploits. All you can do via Intune is import an XML policy, so you'll need to either play around with the Get-ProcessMitigation, Set-ProcessMitigation and ConvertTo-ProcessMitigationPolicy PowerShell cmdlets or use the Security Centre UI (Windows 10 Settings > Update & Security > Windows Security > App & browser control, then Exploit Protection). Configure the settings how you want them then click Export settings to get the XML file for Intune.
Further Reading:
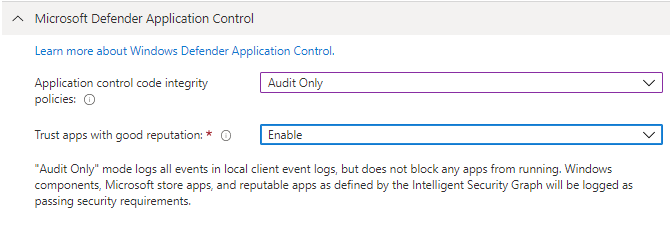
Application Control
With Intune you can only deploy the built in Application Control policy which, when enforced, will only allow Windows components and the Microsoft Store apps to run. If you also trust apps with good reputation you will also be able to run repitable apps, as defined by the Intelligent Security Graph. This can be configured in Audit Only and Enforce modes.
For custom policies you will need to configure a Custom OMA-URI Setting profile, which is touched upon in the Microsoft Docs.
Further Reading:
- Application Control for Windows - Windows security | Microsoft Docs
- Planning and getting started on the Windows Defender Application Control deployment process (Windows 10) - Windows security | Microsoft Docs
Credential Guard
Credential Guard helps protect against malicious software from gaining access to the Local Security Authority process and thus helps prevent them from hijacking kerberos tickets or other tokens such as NTLM hashes. This is done by running an isolated LSA process using virtualization-based security. You'll need Windows 10 64 bit Enterprise or Education in order to use Credential Guard, along with secure boot, TPM and support for virtualization-based security.
All we can configure through Intune is whether it's enabled or not, and whether we're using UEFI lock.
More details can be found on the Microsoft Docs as there's lots of thinking to do around single sign-on and other security considerations.
Security Centre
The Windows Defender Security Centre is accessed via Settings > Update & Security > Windows Security on a Windows 10 device. This set of configuration items will allow you to determine which areas the user can access and also control notifications, TPM settings and custom IT Helpdesk contact details.
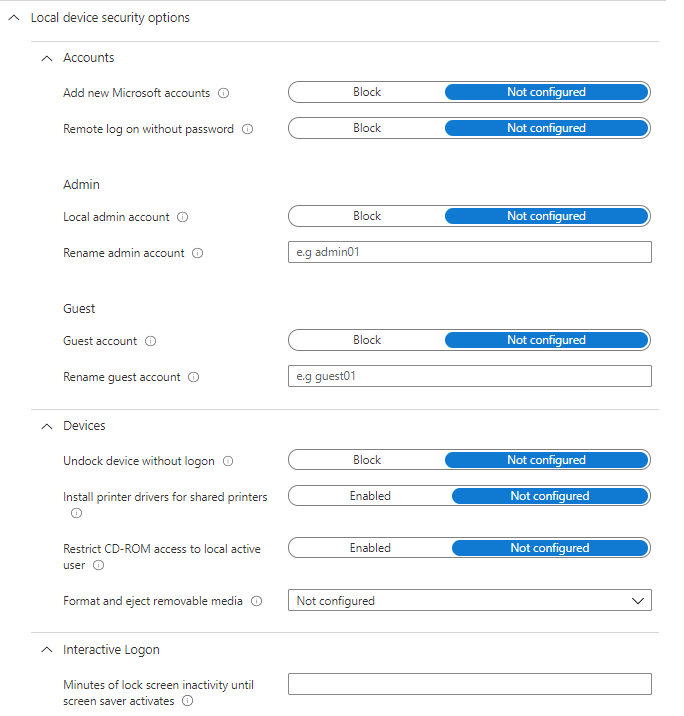
Local device security options
These options are basically like the Local Security policy from Group Policy, and include:
- Accounts - restrict Microsoft accounts, remote access without password, configure local admin and guest accounts
- Devices - unlock without logon, install printer drivers for shared printers, removeable media settings
- Interactive Logon - require Ctrl+Alt+Del, hide last signed-in username, login message
- Network access - Anonymous access controls over Named Pipes, SAM shares, and accounts, LAN Manager hash value policy
- UAC Settings
- MS Network Client/Server - digital signature and SMB policies
In this post
- Introduction
- Application Guard
- Defender Firewall
- Defender SmartScreen
- Windows Encryption
- Exploit Guard
- Application Control
- Credential Guard
- Security Centre
- Local device security options
Support My Work
I hope you find my content useful. Please consider tipping to support the running costs of hosting, licensing etc on my Ko-fi page.